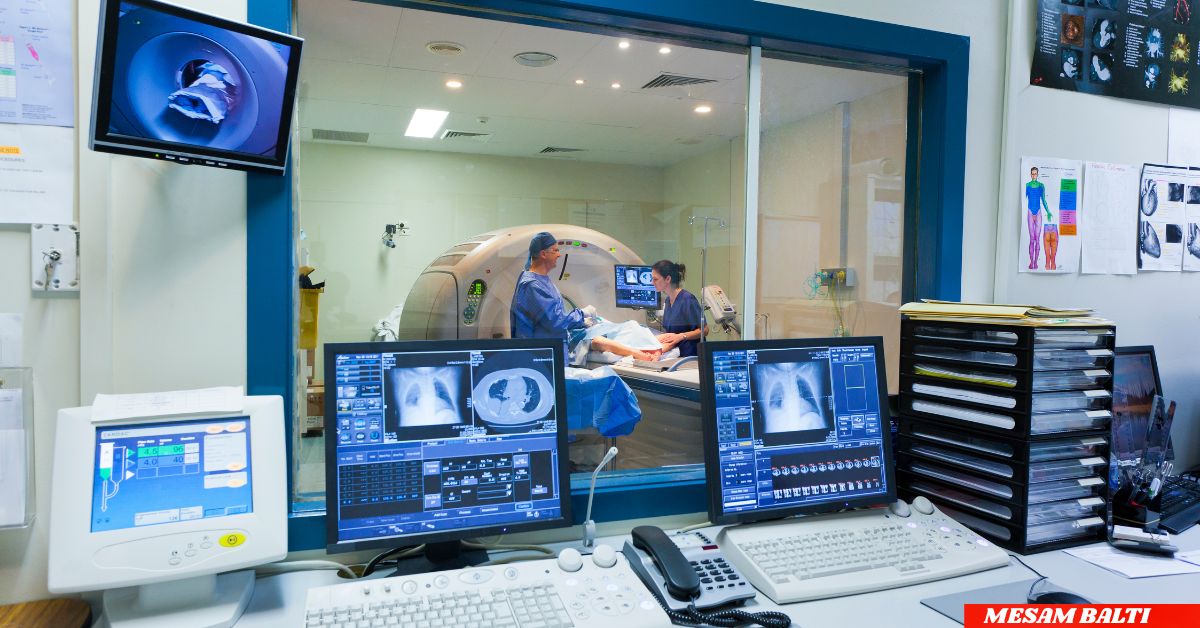
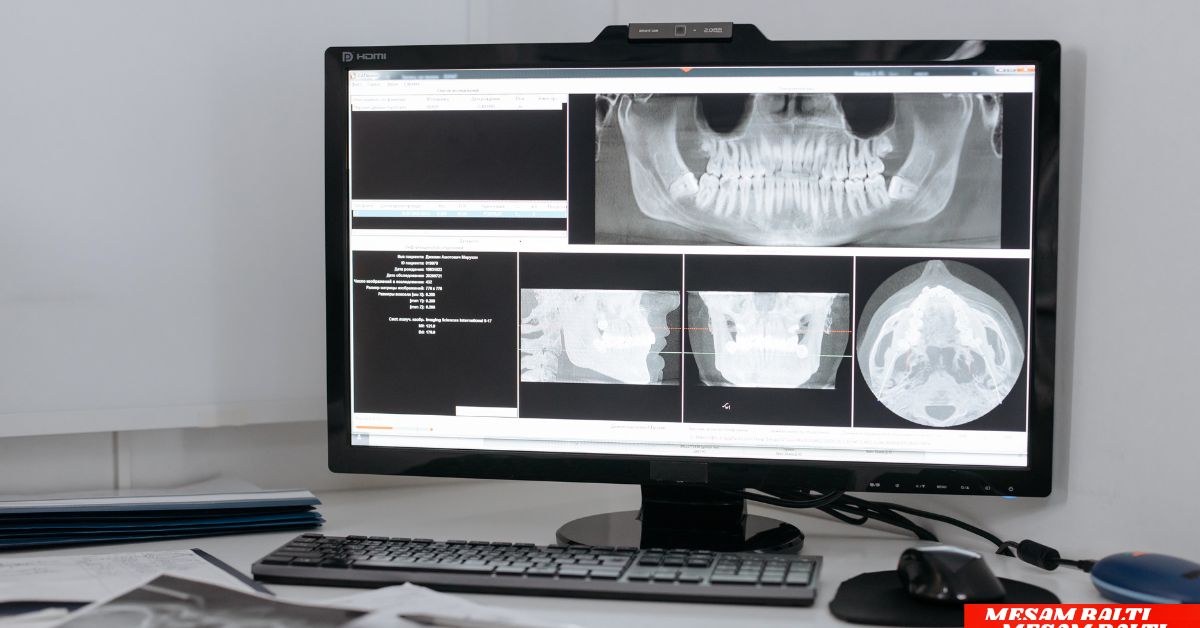
Introduction: The Future of Radiology Has Arrived
In a world that already exists, imagine radiologists able to diagnose diseases more quickly and with pinpoint accuracy, habits that save lives and untold stitches in the doctor’s aisle. That world is no longer a dream — it’s reality, courtesy of AI in radiology: reading X-rays and MRIs faster and better. AI is revolutionising medical imaging, helping radiologists detect abnormalities faster and more accurately than ever EINA_BILD. In this post, we examine how AI is transforming radiology, its advantages, limitations, and where things seem to be headed with this revolutionary tool.
What Is AI in Radiology?
AI in radiology, for one, about how machine learning such as deep learning algorithms are being used to analyze medical images like X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, ultrasounds etc. They are trained on massive data sets of medical images to detect patterns, anomalies, and possible diagnoses that might elude the human eye.
How AI Works in Medical Imaging
- Image Recognition: AI for visual analysis, like convolutional neural networks (CNNs), use pixel data for identifying abnormalities, such as tumors, fractures, or infectious diseases.
- Automation: A.I. can triage urgent cases, by which I mean that zeros and ones can now whittle those wait times for critical diagnoses. Radiologists can deliver results faster, and with more accuracy, by matching human expertise to AI’s processing power.
Pros of AI in Radiology
Here’s what it’s doing:
- Faster Diagnoses: AI can analyze X-rays and M.R.I.s in seconds, highlighting potential problems for radiologists to examine.
- Improved Accuracy: AI cuts down on human error by spotting the subtle patterns that people overlook.
- Enhanced Workflow Efficiency: It triages cases so that it can prioritize the urgent cases — like brain haemorrhages — so that radiologists can look at the sickest patients first.
- Accessibility in Underserved Areas: AI solutions would be able to offer preliminary analysis and fill the void in healthcare coverage.
Applications of AI in Radiology
Case Study: Detecting Lung Cancer
In 2019, Mayo Clinic teamed with an AI company to develop a tool that can spot lung nodules in CT scans with 95% accuracy.
AI in Emergency Rooms
Hospitals including Mount Sinai in New York rely on AI to analyze head CT scans for strokes or brain bleeds.
Breast Cancer Screening
Tools using artificial intelligence such as those developed by iCAD scrutinize mammograms for tasks such as spotting microcalcifications and tumors.
Shortcomings and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence in Radiology
- Quality of Data: AI models are hungry for massive volumes of strong data.
- Regulatory barriers: AI systems need to meet rigorous FDA and internationally recognized requirements.
- Integration: Integrating AI with existing hospital systems can be difficult and expensive.
- Ethical worries: AI is accountable when it is wrong in diagnosis.
The Future of AI in Radiology
- Personalized Medicine: AI could help crunch imaging data using genetic and clinical information to personalize treatments.
- Predictive Analytics: A.I. will be able to predict disease progression by analyzing past imaging data.
- Collaboration with Radiologists: AI will continue to act as a “second set of eyes” augmenting radiologist skill.
- Global Impact: As AI becomes more attainable, it might help democratize health care.
Preparing for AI-Driven Radiology
- Adopt Interoperable Systems: Make sure that hospital systems can talk to AI platforms.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on AI progress and changes to regulation.
- Work with Vendors: Collaborate with trustworthy AI companies.
FAQs
What is AI in radiology?
Radiology uses AI to analyze medical images like X-rays and MRIs to identify abnormalities (tumors, fractures or infections, for example) with speed and accuracy.
Can AI replace radiologists?
AI is meant to help radiologists, not to replace them.
Is AI in radiology safe?
Where the AI tools are trained and validated correctly they are safe and effective.
How artificial intelligence is transforming the analysis of medical images?
AI enhances analysis by detecting subtle patterns, triaging urgent cases, and limiting diagnostic errors.
Conclusion: Applying AI for Improved Healthcare
AI in radiology: Reading X-rays and MRIs faster and better changes healthcare—by speeding and sharpening diagnoses and making them more accessible. From identifying lung cancer to improving emergency-room workflows, A.I. is demonstrating an effect of bringing practical change. There are still obstacles, but the future holds bigger advances that will continue to make radiology a more efficient and effective field than it has ever been.
Want to learn more about AI in health care? Tell us in the comments below or by signing up for our newsletter, which offers the latest news in medical technology.